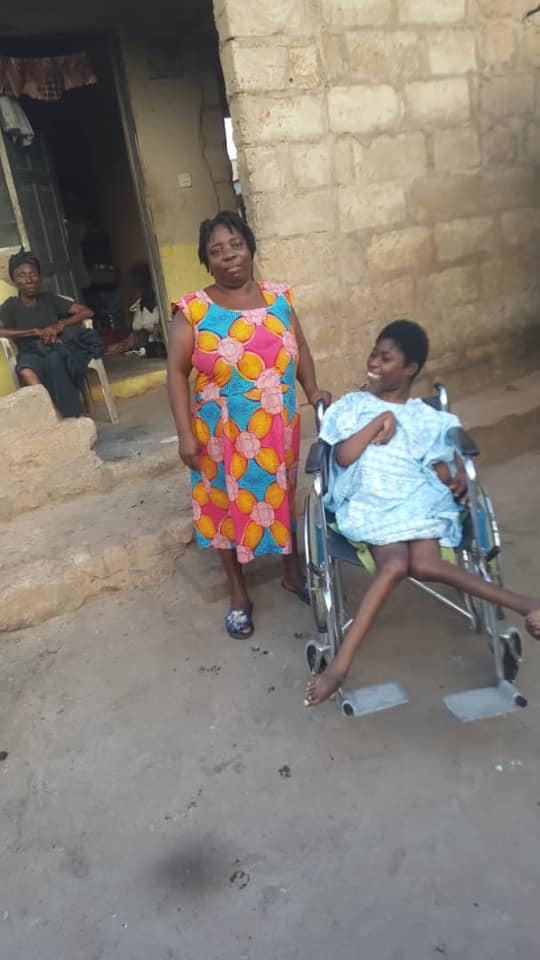
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of permanent disorders affecting movement, posture, and muscle coordination. It's the most common childhood disability, affecting 1 in 300 children.
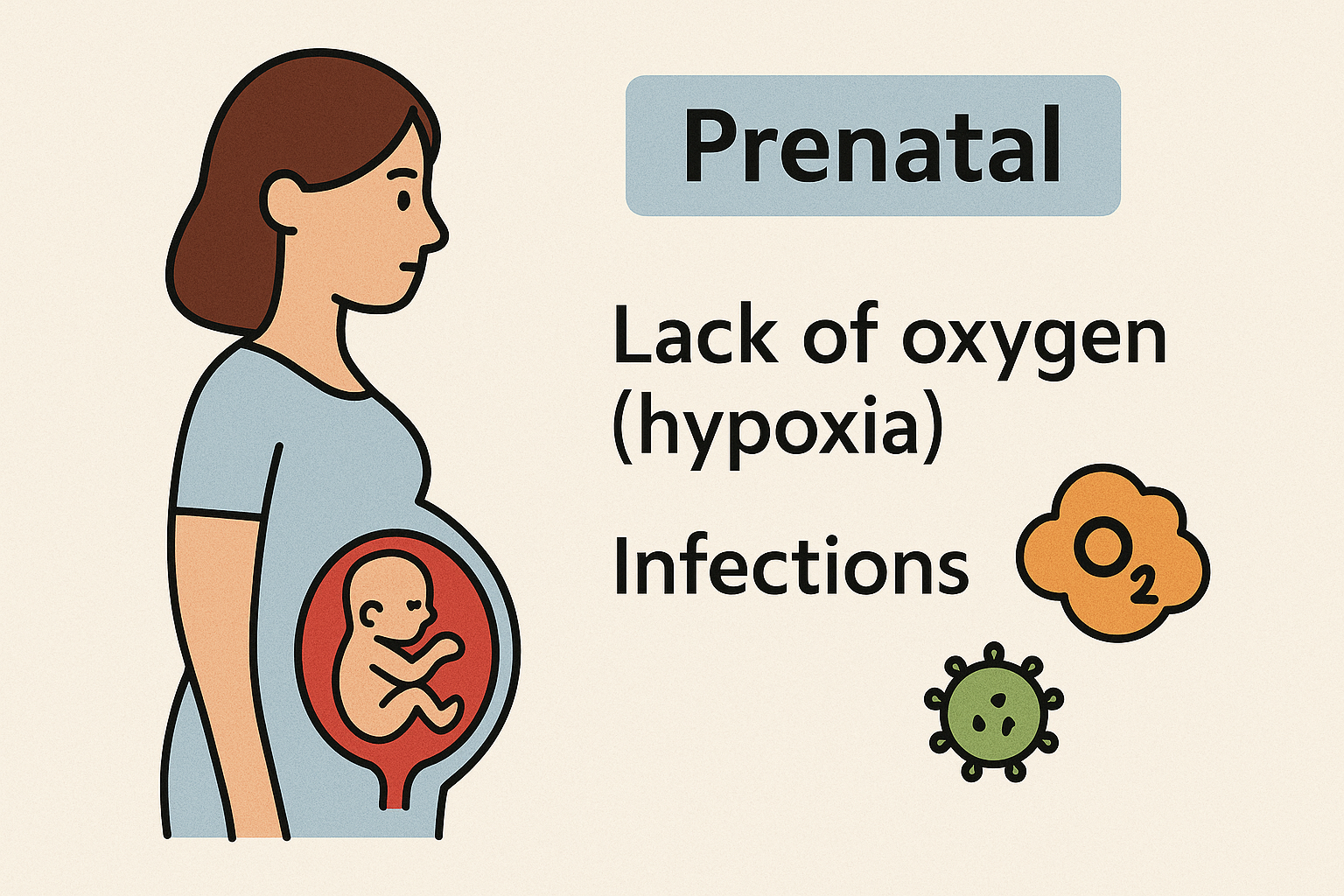
Prenatal Causes (Before Birth Most Common)
Lack of oxygen (hypoxia) to the brain during fetal development. Infections during pregnancy (e.g., rubella, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis). Maternal health issues, like thyroid problems, seizures, or exposure to toxins.
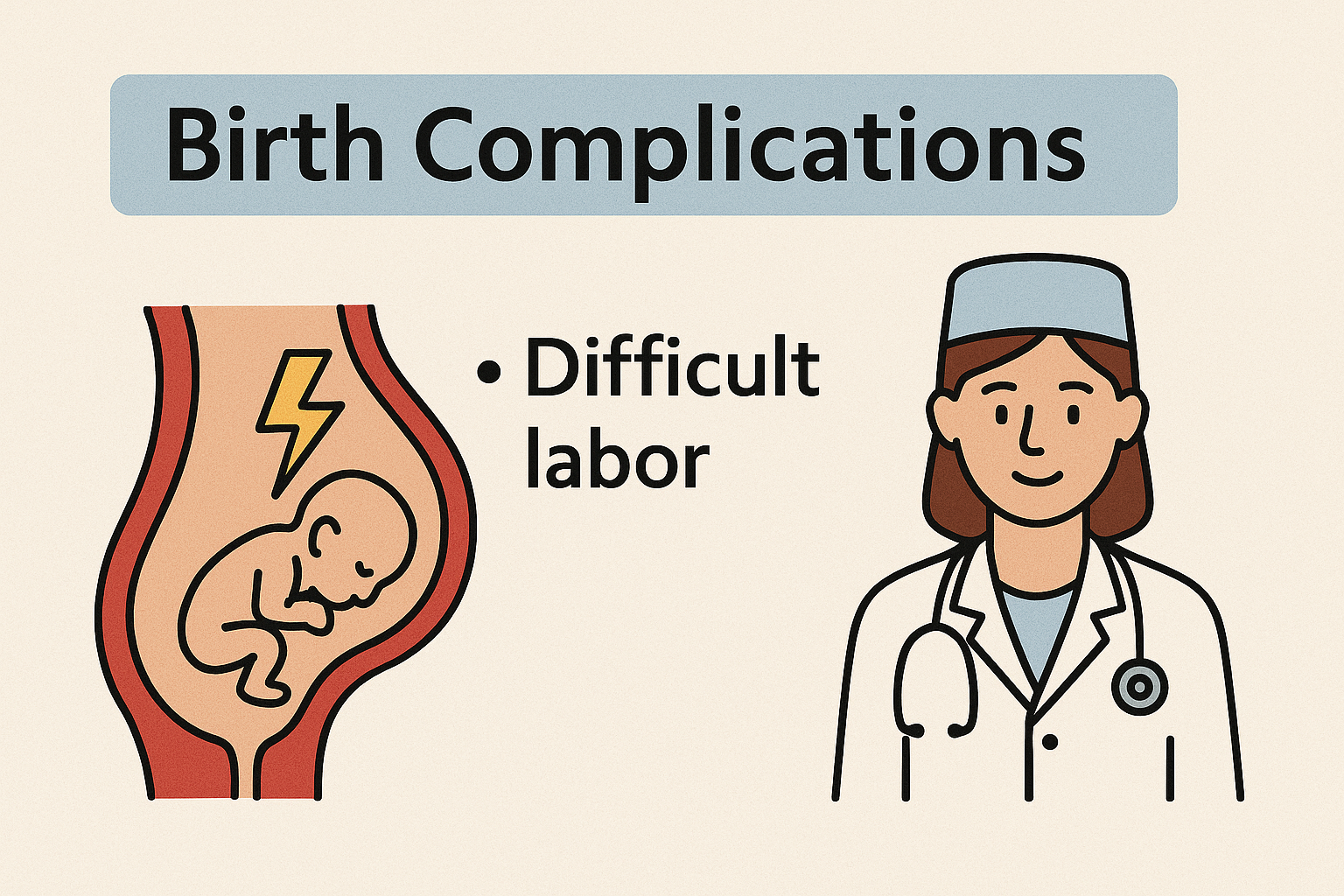
Perinatal Causes (During Birth)
Birth asphyxia – lack of oxygen during delivery. Complicated labor and delivery, including trauma to the baby's head. Infections passed from mother to child during delivery.
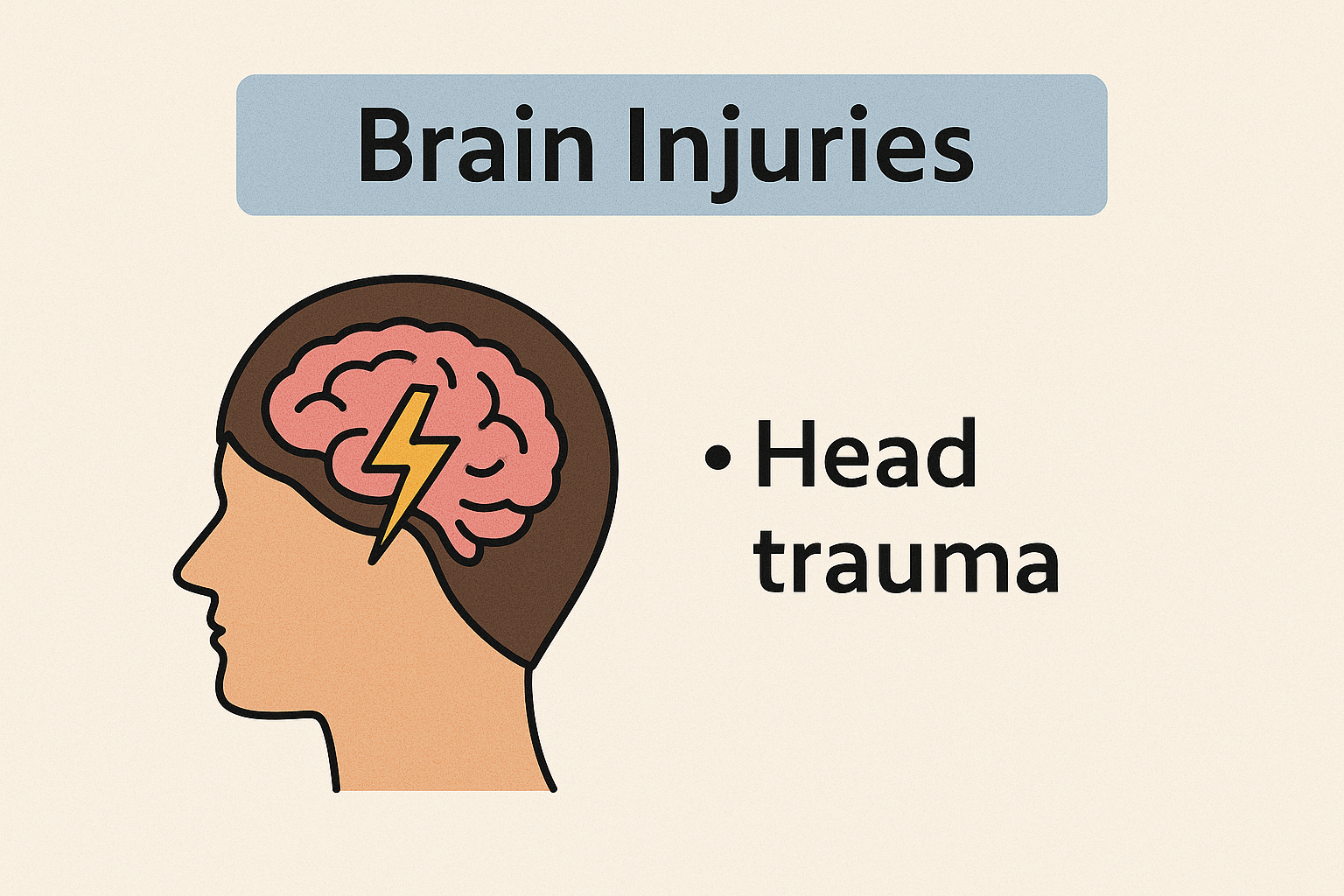
Postnatal Causes (After Birth)
Head injuries (e.g., from accidents or abuse). Brain infections such as meningitis or encephalitis. Severe jaundice in newborns (untreated can lead to brain damage).
Ensure Medical Treatment
Muscle relaxants (e.g., baclofen, diazepam) to reduce spasticity. Anticonvulsants if seizures are present. Botox injections for localized muscle stiffness.
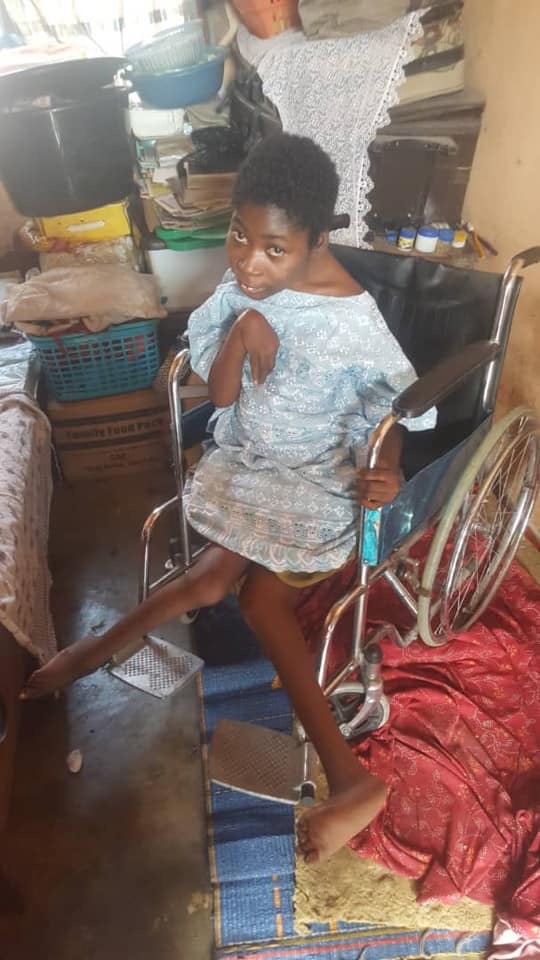
Ensure Medical Treatment
Surgical Treatments Orthopedic surgery: To correct bone or joint deformities. Neurosurgery: For severe cases (e.g., selective dorsal rhizotomy to reduce spasticity
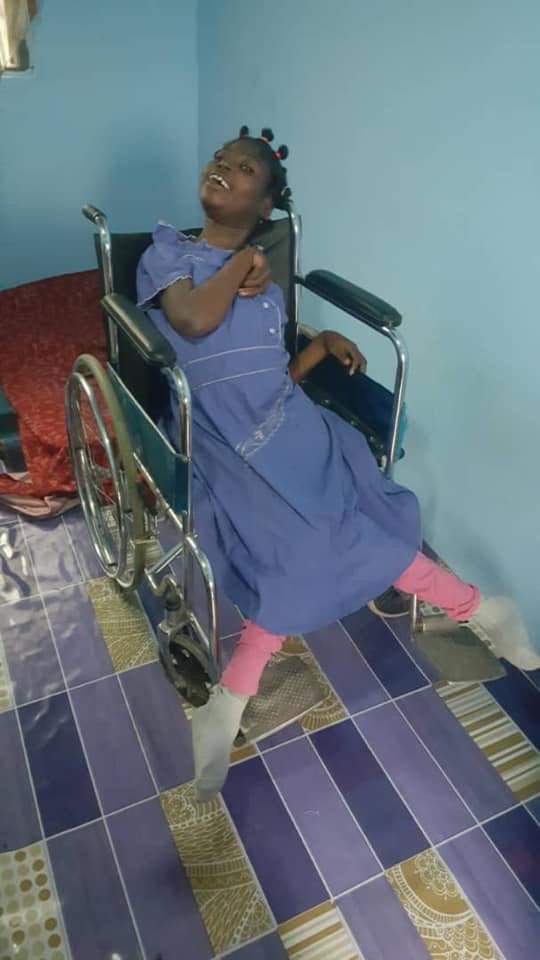
Ensure Medical Treatment
Physical therapy: Improves strength, flexibility, and mobility. Occupational therapy: Helps with daily tasks and independence. Speech and language therap